Heat Conduction Welding
Diode lasers are used in various joining processes in industrial series production. High firmness and low warpage are the characteristics of laser welding with our lasers. Also, at high cutting speeds, excellent seam surfaces at the workpiece can be achieved, with a difference between heat conduction welding and keyhole welding.
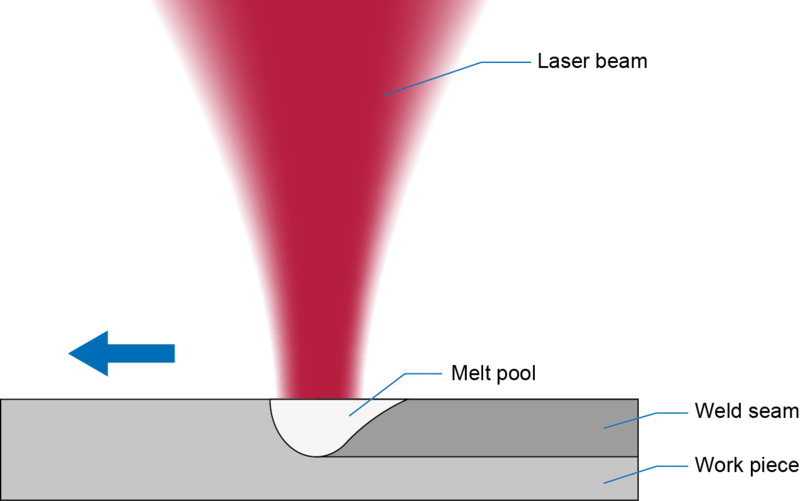
Heat conduction welding with diode lasers is often used at workpieces with low material strength such as thin sheets, foils or wires. The laser beam is absorbed at the workpiece surface and the required energy is led to the workpiece only by heat conduction. The created smooth and rounded welded seam must not be post-processed. The method is, for example, suitable for sheet metal working of materials such as stainless steel, especially for manufacturing products that have high demands for the optical quality of welded seams in the visible field.
Heat conduction welding - the method
Diode conduction welding is characterized by low exposure depths with a maximum of one millimeter and is mainly used for joining sheets with low material thickness. With heat conduction welding, the laser melts the sheets along the intended joint. The melts of the joint partners merge and then cool off to the actual welding seam. Thus, hose connections can be realized more quickly and with lower material distortion than with usual welding methods. Additionally, smooth and pore-free welding seams are created that do not need any post-processing. This makes heat conduction welding, especially in visible areas, the method of choice.
 The process advantages of diode lasers
Laserline’s diode lasers optimize heat conduction welding in a number of ways. The uniform power output and homogeneous intensity distribution (top-hat beam profile) guarantee excellent seam qualities and high process stability. Additionally, there are enormous economical advantages: with a lifetime of more than 30,000 operating hours, besides high efficiency and low maintenance effort, Laserline's diode lasers are clearly superior to the other available beam sources.
Application examples
Sinks
The process advantages of diode lasers
Laserline’s diode lasers optimize heat conduction welding in a number of ways. The uniform power output and homogeneous intensity distribution (top-hat beam profile) guarantee excellent seam qualities and high process stability. Additionally, there are enormous economical advantages: with a lifetime of more than 30,000 operating hours, besides high efficiency and low maintenance effort, Laserline's diode lasers are clearly superior to the other available beam sources.
Application examples
Sinks
 They can be found in every household and every factory canteen, and they always seem to be from one cast, e.g. sinks made of stainless steel. Actually, however, there are welding seams. That you do not see them often has to do with Laserline's diode lasers: they render a technically and economically optimal heat conduction welding possible that leaves no visible marks.
Metal bellows
They can be found in every household and every factory canteen, and they always seem to be from one cast, e.g. sinks made of stainless steel. Actually, however, there are welding seams. That you do not see them often has to do with Laserline's diode lasers: they render a technically and economically optimal heat conduction welding possible that leaves no visible marks.
Metal bellows
 When thermal expansions of pipelines must be compensated or vibrations between vacuum pumps and measuring instruments must be decoupled, metal bellows are used. Welding thin and flexible membrane pairs requires an even heat input that creates stable, crack-free welding seams. Here, Laserline's diode lasers with heat conduction welding provide excellent results.
When thermal expansions of pipelines must be compensated or vibrations between vacuum pumps and measuring instruments must be decoupled, metal bellows are used. Welding thin and flexible membrane pairs requires an even heat input that creates stable, crack-free welding seams. Here, Laserline's diode lasers with heat conduction welding provide excellent results.
 The process advantages of diode lasers
Laserline’s diode lasers optimize heat conduction welding in a number of ways. The uniform power output and homogeneous intensity distribution (top-hat beam profile) guarantee excellent seam qualities and high process stability. Additionally, there are enormous economical advantages: with a lifetime of more than 30,000 operating hours, besides high efficiency and low maintenance effort, Laserline's diode lasers are clearly superior to the other available beam sources.
Application examples
Sinks
The process advantages of diode lasers
Laserline’s diode lasers optimize heat conduction welding in a number of ways. The uniform power output and homogeneous intensity distribution (top-hat beam profile) guarantee excellent seam qualities and high process stability. Additionally, there are enormous economical advantages: with a lifetime of more than 30,000 operating hours, besides high efficiency and low maintenance effort, Laserline's diode lasers are clearly superior to the other available beam sources.
Application examples
Sinks
 They can be found in every household and every factory canteen, and they always seem to be from one cast, e.g. sinks made of stainless steel. Actually, however, there are welding seams. That you do not see them often has to do with Laserline's diode lasers: they render a technically and economically optimal heat conduction welding possible that leaves no visible marks.
Metal bellows
They can be found in every household and every factory canteen, and they always seem to be from one cast, e.g. sinks made of stainless steel. Actually, however, there are welding seams. That you do not see them often has to do with Laserline's diode lasers: they render a technically and economically optimal heat conduction welding possible that leaves no visible marks.
Metal bellows
 When thermal expansions of pipelines must be compensated or vibrations between vacuum pumps and measuring instruments must be decoupled, metal bellows are used. Welding thin and flexible membrane pairs requires an even heat input that creates stable, crack-free welding seams. Here, Laserline's diode lasers with heat conduction welding provide excellent results.
When thermal expansions of pipelines must be compensated or vibrations between vacuum pumps and measuring instruments must be decoupled, metal bellows are used. Welding thin and flexible membrane pairs requires an even heat input that creates stable, crack-free welding seams. Here, Laserline's diode lasers with heat conduction welding provide excellent results.
